Mazda promised us back in October they’d be bringing this smooth looking Takeri concept to the Tokyo Motor Show. At the time they were a bit hush-hush on the finer details. Now that the Tokyo show is here they’ve given us a few more pics and a new video, but still not much else.
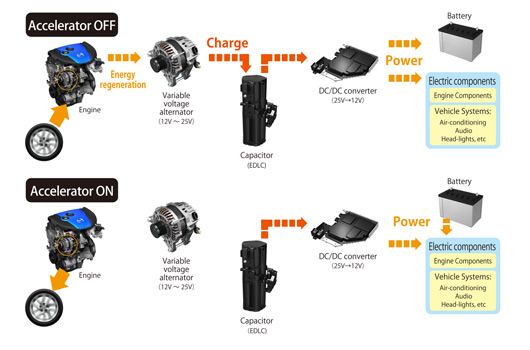
One thing they have gone into is the regenerative braking system, rather obtusely labelled ‘i-ELOOP’—that’s intelligent energy loop for those playing at home. This technology will feature on road cars next year, Mazda say.
Real world use is expected to yield a 10% reduction in fuel consumption. Here’s the neat bit for all the gadget freaks out there, instead of using a battery to store the recaptured energy Mazda has employed a capacitor to do the work. It can be fully charged in less than a minute and is better suited to the demands of rapid charging/discharging.
Mazda ‘i-ELOOP’ World’s First Capacitor-Based Regenerative Braking System
Mazda Motor Corporation has developed the world’s first passenger vehicle regenerative braking system that uses a capacitor. The groundbreaking system, which Mazda calls ‘i-ELOOP’, will begin to appear in Mazda’s vehicles in 2012. In real-world driving conditions with frequent acceleration and braking, ‘i-ELOOP’ improves fuel economy by approximately 10 percent.
Mazda’s regenerative braking system is unique because it uses a capacitor, which is an electrical component that temporarily stores large volumes of electricity. Compared to batteries, capacitors can be charged and discharged rapidly and are resistant to deterioration through prolonged use.
‘i-ELOOP’ efficiently converts the vehicle’s kinetic energy into electricity as it decelerates, and uses the electricity to power the climate control, audio system and numerous other electrical components.
Regenerative braking systems are growing in popularity as a fuel saving technology. They use an electric motor or alternator to generate electricity as the vehicle decelerates, thereby recovering a portion of the vehicle’s kinetic energy. Regenerative braking systems in hybrid vehicles generally use a large electric motor and dedicated battery.
Mazda examined automobile accelerating and decelerating mechanisms and developed a highly efficient regenerative braking system that rapidly recovers a large amount of electricity every time the vehicle decelerates. Unlike hybrids, Mazda’s system avoids the need for a dedicated electric motor and battery.
‘i-ELOOP’ features a new 12-25V variable voltage alternator, a low-resistance electric double layer capacitor and a DC/DC converter. ‘i-ELOOP’ starts to recover kinetic energy the moment the driver lifts off the accelerator pedal and the vehicle begins to decelerate. The variable voltage alternator generates electricity at up to 25V for maximum efficiency before sending it to the Electric Double Layer Capacitor (EDLC) for storage.
The capacitor, which has been specially developed for use in a vehicle, can be fully charged in seconds. The DC/DC converter steps down the electricity from 25V to 12V before it is distributed directly to the vehicle’s electrical components.
The system also charges the vehicle battery as necessary. ‘i-ELOOP’ operates whenever the vehicle decelerates, reducing the need for the engine to burn extra fuel to generate electricity. As a result, in “stop-and-go†driving conditions, fuel economy improves by approximately 10 percent.
The name ’i-ELOOP’ is an adaptation of “Intelligent Energy Loop†and represents Mazda’s intention to efficiently cycle energy in an intelligent way.
‘i-ELOOP’ also works in conjunction with Mazda’s unique ‘i-stop’ idling stop technology to extend the period that the engine can be shut off.
Mazda is working to maximize the efficiency of internal combustion engine vehicles with its groundbreaking SKYACTIV TECHNOLOGY. By combining this with i-stop, i-ELOOP and other electric devices that enhance fuel economy by eliminating unnecessary fuel consumption, Mazda is striving to deliver vehicles with excellent environmental performance as well as a Zoom-Zoom ride to all its customers.
Mazda TAKERI to premiere at 2011 Tokyo Motor Show
Hiroshima, Japan, 25 October 2011. Mazda Motor Corporation will showcase the global premiere of the Mazda TAKERI concept car, a next-generation midsized sedan, at the 42nd Tokyo Motor Show. Also on stage making its Japan debut will be the new CX-5 crossover SUV – equipped with the full array of Mazda’s breakthrough SKYACTIV TECHNOLOGY – along with new technologies and production models.
Mazda’s theme for the 2011 Tokyo Motor Show is “Environmental Technology, Pushing the Boundaries of the Emotion of Motion. As long as there are people who love to drive, Mazda will continue to evolve the emotion of motion in harmony with environmental and safety performance.â€
The TAKERI concept exploits Mazda’s new design language, KODO – Soul of Motion, to bring a new level of strength and allure to sedan styling. Under this appealing exterior is benchmark SKYACTIV TECHNOLOGY like Mazda’s first regenerative braking system that converts kinetic energy to electricity during deceleration, stores it in capacitors and then uses it to power the vehicle’s electric equipment, thereby reducing load on the engine and saving fuel. This – combined with the new SKYACTIV-D diesel engine, Mazda i-stop, new lightweight, aerodynamic and chassis technologies – enable the Mazda TAKERI to achieve excellent fuel economy with vigorous performance and a comfortable ride.












2 replies on “Tokyo 2011: Mazda Takeri concept”
[…] Mazda Takeri Concept […]
[…] a look at the car in full detail. Based on the ‘Kodo’ design language of the stylish Takeri concept, the translation from free reign to production reality has seen some […]